vSAN Deployment Options
This is part of the VMware vSAN guide post series. By using the following link, you can access and explore more objectives from the VMware vSAN study guide.
In the previous two posts of this series, we explored the world of VMware vSAN and familiarized ourselves with crucial terminology associated with this product. Now, let’s take the next step by addressing a few key questions: If you’re interested in deploying vSAN, you might wonder about the various types of deployments available. Additionally, you might be curious to find out which deployment option aligns most effectively with the specific needs of your organization. Furthermore, it’s important to understand the benefits and considerations associated with each deployment type. Join me in this guide as we explore the different vSAN deployment options.
As mentioned in the previous posts, vSAN aggregates local storage devices to create a single storage pool shared across all hosts in a vSAN cluster. To utilize this functionality, you must first create a cluster and then enable vSAN on it. Now, let’s explore the various methods available for building a vSAN cluster.
There are two ways to build a vSAN cluster: you can either utilize vSAN ReadyNodes or construct a User-Defined vSAN cluster by selecting individual software and hardware components, including drivers, firmware, storage I/O controllers, and so on.
1- vSAN ReadyNode
The vSAN ReadyNode is a preconfigured solution provided by VMware partners such as Cisco, Dell, Fujitsu, IBM, and Supermicro. These partners have collaborated with VMware to offer validated server configurations that are specifically designed and tested for vSAN deployment. By choosing a vSAN ReadyNode, you can benefit from a hardware setup that is recommended by both the server OEM and VMware.
The advantage of using a vSAN ReadyNode is that it provides a streamlined and simplified approach to deploying vSAN. The hardware and software components have been prevalidated to ensure compatibility and optimal performance with vSAN. This saves you time and effort in selecting individual hardware components and ensures a smooth and efficient deployment process.
To explore the specific offerings and configurations available from each partner, you can visit the VMware vSAN ReadyNode Sizer website. The Sizer enables you to size factors in storage, compute, memory, and IOPS in the logic to provide you with the most optimized vSAN recommendation.
https://vsansizer.esp.vmware.com/

The vSAN ReadyNode Sizer tool helps administrators determine the appropriate hardware configuration for their vSAN deployment based on factors such as workload requirements, performance goals, and budget constraints. It considers factors like the number of virtual machines, storage capacity, IOPS (Input/Output Operations Per Second) requirements, and redundancy levels to recommend a suitable hardware configuration.
By using the vSAN ReadyNode Sizer tool, administrators can ensure that the hardware they choose meets the compatibility and performance requirements of vSAN, resulting in an optimized and well-sized infrastructure for their virtualized environment. The tool provides guidance on the specific server models, CPU, memory, storage devices, and network adapters that are certified and recommended by VMware for use with vSAN.
The vSAN ReadyNode Sizer simplifies the process of designing and selecting hardware components for vSAN deployments, helping administrators make informed decisions and achieve optimal performance and scalability for their virtualized storage infrastructure.
Some important benefits of using vSAN Ready Nodes are as follows:
- Compatibility and Certification: vSAN Ready Nodes undergo rigorous testing and certification processes by VMware. This ensures the hardware and software components are fully compatible with vSAN and meet the required performance standards.
- Simplified Deployment: Since vSAN Ready Nodes are pre-configured and certified, the deployment process becomes more streamlined. This reduces the time and effort required for hardware selection, compatibility testing, and system integration.
- Performance Optimization: vSAN Ready Nodes are designed and optimized to deliver high-performance storage for virtualized environments. The hardware configurations are carefully chosen to maximize the performance of vSAN and provide efficient storage operations.
- Scalability and Flexibility: vSAN Ready Nodes are available in various configurations, ranging from entry-level to high-performance systems. This allows organizations to choose the appropriate hardware that meets their specific requirements and easily scale their storage infrastructure as needed.
- Vendor Support: By using vSAN Ready Nodes, organizations can leverage support from both VMware and hardware vendors. This ensures that in case of any issues, there is a coordinated support mechanism to address them.
At the time of writing this blog, the only supported deployment for vSAN ESA (Express Storage Architecture) is vSAN ReadyNodes
Organizations should consider vSAN Ready Nodes if they are planning to deploy VMware vSAN as their storage solution. The program provides a validated and optimized hardware platform, simplifies the deployment process, and ensures compatibility and performance. This can result in faster time to value, improved operational efficiency, and reduced risk in implementing a software-defined storage solution.
2-User-Defined vSAN Cluster
The second option is to build a vSAN cluster by selecting individual software and hardware components, such as drivers, firmware, and storage I/O controllers. Actually, it involves building a storage infrastructure using individual server hardware components of your choice. Instead of using vSAN Ready Nodes, you select and configure servers, CPUs, memory, network adapters, and storage devices independently, based on your specific requirements and preferences.
The main advantages of a user-defined vSAN cluster include:
- Flexibility: You have complete control over hardware selection, allowing you to tailor the configuration to meet your specific performance, capacity, and budget requirements.
- Scalability: You can scale the cluster by adding servers and storage devices according to your needs, without being limited to predefined configurations.
- Cost optimization: User-defined clusters offer the potential for cost savings by selecting hardware components based on competitive pricing or repurposing existing infrastructure.
But one of the challenging aspects of setting up a user-defined vSAN is ensuring the compatibility of all hardware and software components. Before you start building the cluster, it is important to thoroughly check and verify the compatibility of each component, including drivers, firmware, storage I/O controllers, servers, memory, and flash devices. This verification process ensures that the components have been tested and certified for compatibility with vSAN.
To access the comprehensive compatibility information, you can visit the vSAN compatibility guide website at http://www.vmware.com/resources/compatibility/search.php.
It is crucial to review this information on the VMware compatibility guide website to ensure that the components you choose are officially supported by vSAN. By adhering to the guidelines and selecting components from the compatibility list, you can build a vSAN cluster that is tailored to your specific requirements. This is one of the significant reasons why you should consider using vSAN ReadyNodes.
It’s important to note that vSAN EXpress Storage Architecture (ESA) is currently not officaly supported for user-defined cluser. The only avilable option is to use vSAN ReadyNodes!
Now that you have come up with one way to build the cluster, it’s time to decide which deployment method suits our organization and requirements. There are three different supported deployment options for vSAN clusters:
- Standard vSAN Cluster
- Two-Node vSAN Cluster
- vSAN Stretched Cluster
Standard vSAN Cluster
The standard vSAN cluster serves as the fundamental deployment type for most organizations. It consists of a minimum of three hosts located at the same site and connected through a Layer 2 network. Suppose you have a data center with three VMware hosts, each equipped with local storage. By configuring them as a standard vSAN cluster, you can aggregate their storage resources into a shared, highly available storage pool.
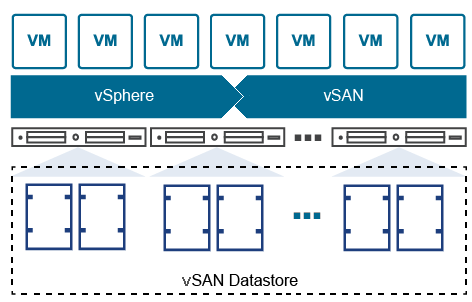
This type of deployment is well-suited for general-purpose workloads as it offers scalability, high performance, and fault tolerance within a single site. However, it’s important to note that since all hosts reside in the same location, the standard vSAN cluster lacks geographical redundancy, which makes it vulnerable to failures at the site level.
Two-Node vSAN Cluster
Designed for remote office/branch office (ROBO) environments, the two-node vSAN cluster offers high availability within a limited infrastructure. This deployment type consists of two hosts at the same site, connected either through a network switch or directly. Let’s say you have a small branch office with limited space and resources. You can set up a two-node vSAN cluster using two hosts in the branch office and a third host acting as a witness in the main data center. This configuration provides high availability for critical workloads at the branch office.
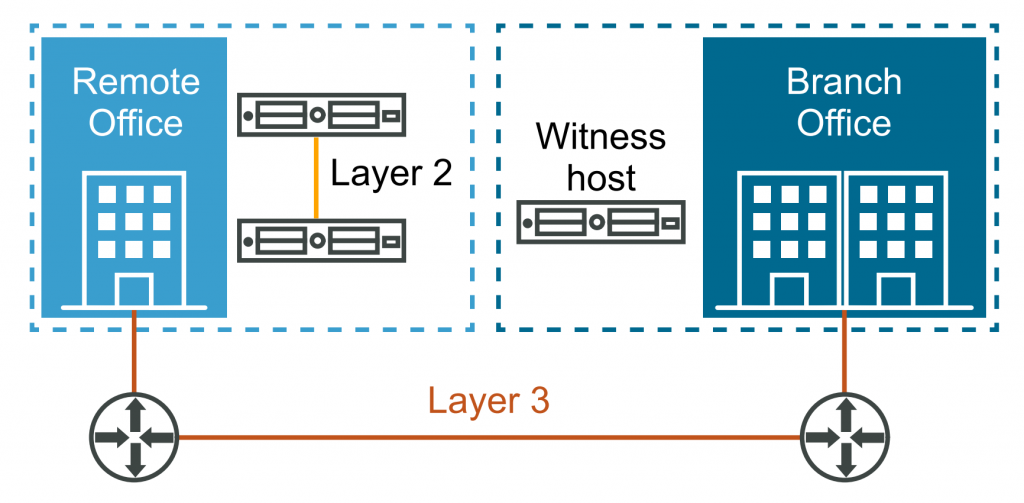
This deployment type is suitable for ROBO environments or scenarios with limited infrastructure, such as retail stores and branch offices. It is particularly advantageous for smaller workloads as it requires fewer hosts, thus reducing infrastructure costs. The witness host plays a crucial role by providing a quorum for the two nodes in the cluster, located at the remote office, and it operates with minimal bandwidth requirements.
However, it’s important to note that the two-node cluster may have limitations when it comes to scaling up to accommodate significant workload growth. Adding more hosts to this cluster is not possible, and therefore, transitioning from a two-node cluster to a three or more nodes cluster becomes necessary for further scalability.
vSAN Stretched Cluster
A vSAN stretched cluster extends across two geographically separate sites, providing resiliency against the loss of an entire site. The hosts are evenly distributed between the two sites, and a witness host is located at a third site to provide the witness function. The vSAN stretched cluster is ideal for organizations that require data availability across multiple sites.
Imagine you have two data centers in different cities, and you want to ensure continuous availability and data protection in case one site goes down. By deploying a vSAN stretched cluster, you can distribute your hosts and storage resources across both sites while maintaining synchronization and failover capabilities.
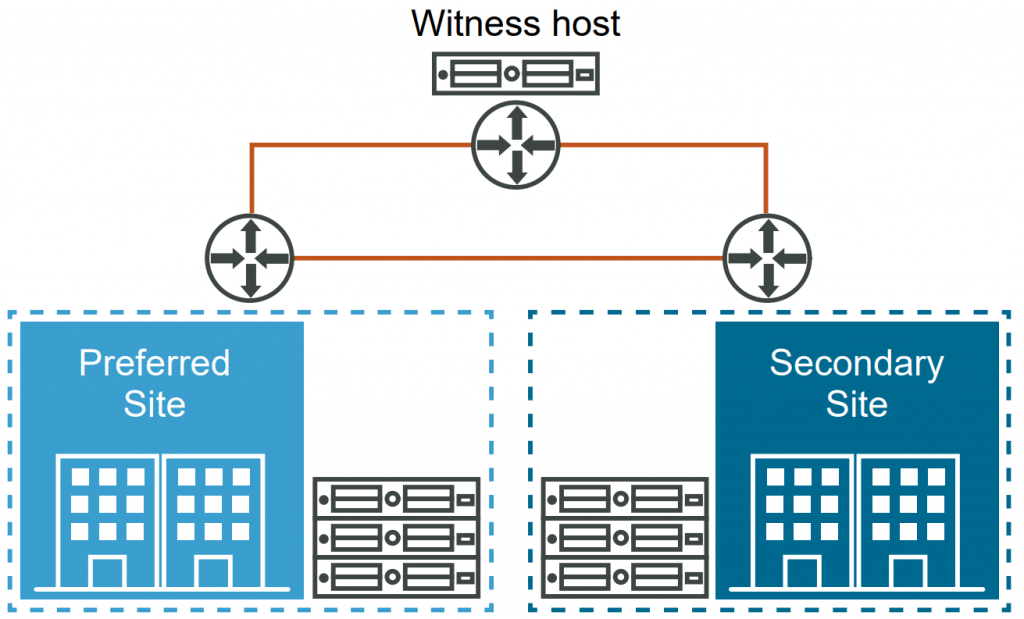
This deployment type is ideal for scenarios where high availability and disaster recovery are crucial. It ensures the protection of data at the primary site by replicating it across the secondary site. To achieve this, it requires a high network bandwidth and low network latency (within 5 ms) between the two data sites. Since a witness host acts as a tie-breaker, storing only metadata, requires minimum bandwidth.
Conclusion
Now, we have learned about the various types of vSAN deployments. Each deployment type of vSAN offers unique advantages and considerations such as scalability, performance, geographical redundancy, and disaster recovery, and you should take into account these features in order to determine the most suitable vSAN deployment option.
As I don’t have access to vSAN ReadyNodes in my lab, I will go with the second option which is a user-defined vSAN cluster.
In the next post, I will explore deeper into the requirements and considerations of each deployment type.
Stay tuned for more updates!























