vSAN 8: Requirements and considerations
This is part of the VMware vSAN guide post series. By using the following link, you can access and explore more objectives from the VMware vSAN study guide.
As mentioned earlier, vSAN is a cluster feature similar to other cluster features such as High Availability (HA) and Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS) which are implemented and enabled at the cluster level. This means that vSAN operates and manages storage resources collectively across all the hosts within a cluster.
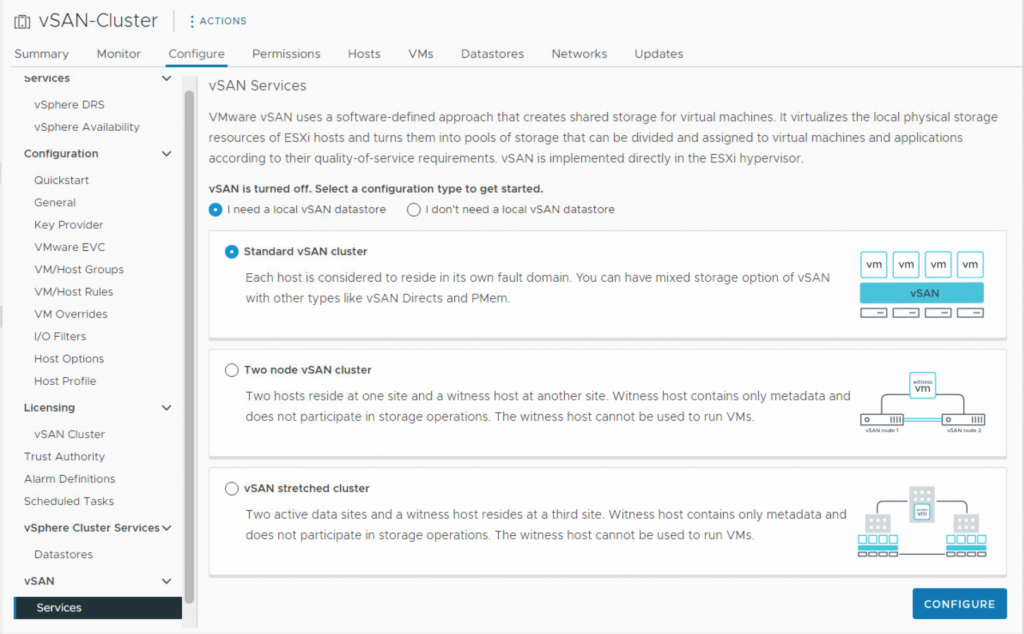
Enabling vSAN at the cluster level facilitates the establishment of a shared storage pool by utilizing the local storage devices of each host within the cluster. However, before enabling the vSAN feature, it is crucial to verify that the cluster and environment fulfill all the necessary requirements. These requirements differ based on the chosen architecture: the Original Storage Architecture (OSA) or the Express Storage Architecture (ESA). Additionally, the type of deployment (Standard, Two-Node, Stretched) determines the specific requirements needed, which may vary in complexity and scale. In this blog post, I will explore the vSAN 8 requirements, focusing on different types of deployments and their respective considerations.
Hardware Requirements
The following requirements are common to all three deployment types (Standard, Two-Node, Stretched), regardless of which one is being used. Therefore, it is essential for the environment to fulfill these requirements. The following table outlines requirements for both hybrid and all-flash clusters in the Original Storage Architecture (OSA).
| Original Storage Architecture (OSA) | Hybrid vSAN Cluster | All-Flash Cluster |
| Storage Device Requirements | All capacity devices, drivers, and firmware versions must be certified and compatible according to VMware Compatibility Guide. | |
| A RAID controller that is in passthrough mode or RAID 0 mode. | ||
| 1- One SSD or PCIe flash device is required for the cache tier (with a capacity of at least 10 percent of the storage consumed on the capacity devices, excluding replicas like mirrors). 2- One magnetic is required for the capacity tier. | 1- One SSD or PCIe flash device is required for the cache tier 2-One SSD or PCIe flash device is required for capacity tier | |
| Host Memory Requirements | Depending on the number of disk groups and devices – use the sizing tool to estimate memory consumption – see vsansizer.vmware.com. | |
| Flash Boot Devices Requirements | For new installations, VMware strongly recommends using devices like M.2, SSDs instead of USB/SD Cards. | |
| Networking Requirements | A minimum dedicated bandwidth of 1 Gbps. | A minimum bandwidth of 10 Gbps, either dedicated or shared. |
| All hosts in your vSAN cluster must be connected to a vSAN Layer 2 or Layer 3 network. | ||
The following table outlines the requirements for an all-flash cluster in the Express Storage Architecture (ESA). Please note that in this architecture, only an all-flash cluster is available.
| Express Storage Architecture (OSA) | All-Flash Cluster |
| Storage Device Requirements | All capacity devices, drivers, and firmware versions must be certified and compatible according to VMware Compatibility Guide. |
| A RAID controller that is in passthrough mode or RAID 0 mode. | |
| Each storage pool must have at least four NVMe TLC devices | |
| Host Memory Requirements | The host itself requires a minimum of 512 GB of memory. However, for vSAN, the memory requirement depends on the number of devices present in the host’s storage pool- see vsansizer.vmware.com/ |
| Flash Boot Devices Requirements | For new installations, VMware strongly recommends using devices like M.2, SSDs instead of USB/SD Cards |
| Networking Requirements | 1- A minimum bandwidth of 25 Gbps, either dedicated or shared 2- All hosts in your vSAN cluster must be connected to a vSAN Layer 2 or Layer 3 network. |
Software Requirments
- Consistent ESXi Version: All ESXi hosts within the vSAN cluster must be running the same version. This ensures compatibility and avoids potential issues arising from mixed ESXi versions.
- vCenter Compatibility: The vCenter server managing the vSAN cluster can be of a higher version than ESXi. This allows for flexibility in upgrading vCenter independently while maintaining the stability and functionality of the vSAN environment.
License Requirments
After meeting all the aforementioned requirements and successfully setting up a vSAN cluster, it is essential to assign the cluster an appropriate vSAN license. There are two main types of vSAN licenses available:
- Subscription Licensing: VMware vSAN can be licensed on a per Core metric and is offered across Standard, Advanced, Enterprise, and vSAN+ editions.
- Perpetual Licensing: VMware vSAN can be licensed per CPU, per concurrent user in 10 or 100 license packs for virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI), and per virtual machine (VM) in 25-VM license packs for remote office/branch office (ROBO) implementations. vSAN Standard, Advanced, and Enterprise editions can be licensed on these three metrics except for vSAN Enterprise Plus, which is only available on a per-CPU license.
Each of these options includes various types, and I highly recommend you refer to this VMware official document for more information. I understand that it can be a bit complicated. If you require assistance with vSAN licensing, it is crucial to consult with experts who can guide you through the process and help you make informed decisions. Our team at ITQ consists of VMware-certified professionals who are here to provide you with customized consultation services, ranging from initial consulting to deployment.
Now, I will discuss several considerations regarding the deployment types you choose for your environments.
Considerations
1- Standard vSAN Cluster
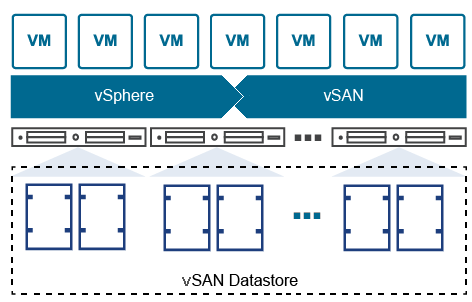
When planning for a standard deployment of vSAN, it is crucial to take into account several fundamental prerequisites in addition to the above requirements:
- vSAN requires a minimum of three ESXi hosts in the cluster
- The network round-trip latency between the hosts should not exceed 1 millisecond.
- It is recommended to have a minimum of 10 Gbps dedicated network connectivity to achieve optimal performance.
2- Two-Node vSAN Cluster
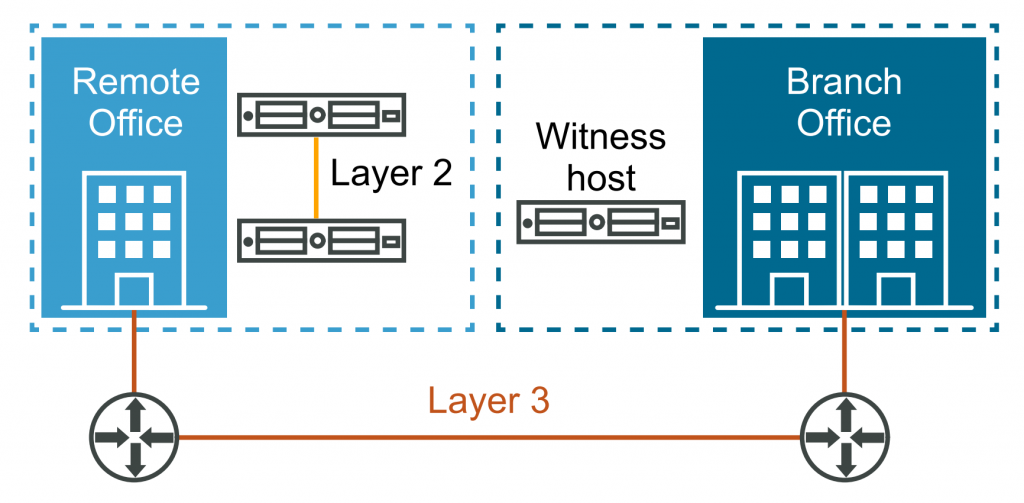
For remote office and branch office (ROBO) deployments with limited resources, vSAN offers a 2-node configuration. The following requirements should be considered for this type of deployment:
- vSAN requires two ESXi hosts in the cluster
- A vSAN Witness Appliance is utilized to provide the necessary quorum in a 2-node configuration. It can be deployed as a virtual machine or on a hardware appliance. it is recommended to deploy the vSAN Witness Appliance in a secondary location, however, it can be deployed on an alternate host within the same site.
- The network round-trip latency between the hosts should not exceed 1 millisecond.
- The network round-trip latency between the hosts and the witness host should not exceed 200 milliseconds.
3- vSAN Stretched Cluster
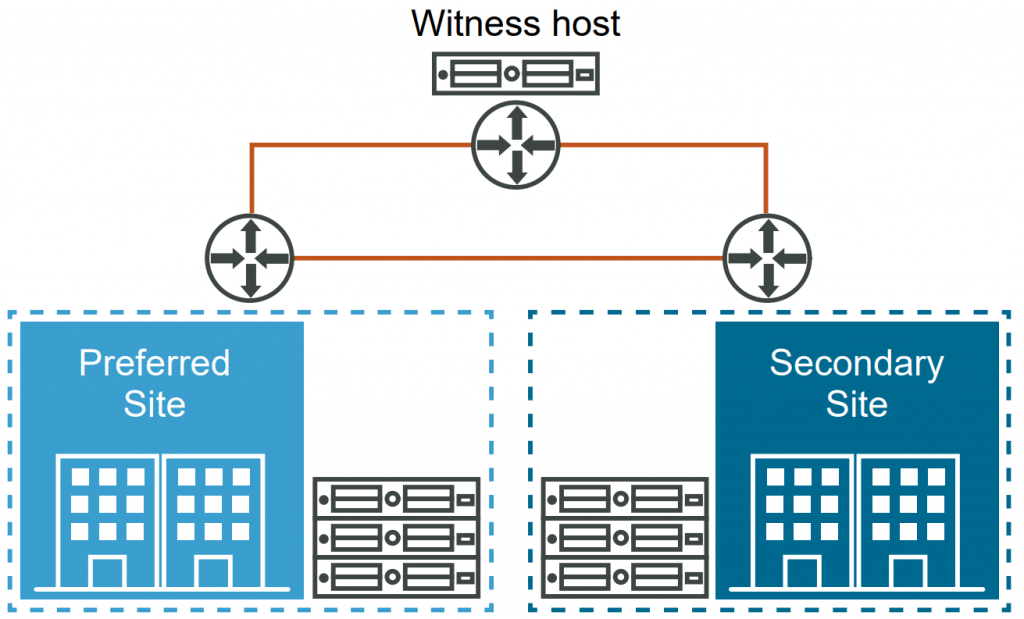
vSAN stretched cluster allows organizations to achieve high availability across geographically dispersed locations. To implement a Stretched Cluster, the following additional requirements must be met:
- A vSAN Witness Appliance is required to provide the necessary quorum in a stretched cluster configuration. It can be deployed as a virtual machine or on a hardware appliance. It should be deployed in a third location that is separate from the primary and secondary sites but has connectivity to both sites.
- The network round-trip latency between the hosts should not exceed 1 millisecond.
- The network round-trip latency between the sites should not exceed 5 milliseconds. A low-latency, high-bandwidth network connection is crucial for maintaining synchronous data replication.
- The network round-trip latency between sites (primary and secondary) and the witness host should be kept below 200 milliseconds.
Deploying a successful vSAN environment requires careful planning and consideration of the essential requirements. By ensuring your hardware is compatible, software versions are up to date, networks are properly configured, and storage policies are appropriately defined, you can leverage vSAN’s power to build a resilient, scalable, and cost-effective software-defined storage infrastructure. I think we have discussed enough about the requirements and considerations for each type of deployment, it is time to prepare for the setup phase.
See you soon!























